Fixed vs. Adjustable-Rate Mortgage: Which One Is Right for You?
Choosing the right mortgage is a big part of buying a home. One of the most important decisions is whether to go with a fixed-rate or an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM). Each has pros and cons, and the right one depends on your financial goals. Here’s a simple guide to help you decide.
1. What Is a Fixed-Rate Mortgage?
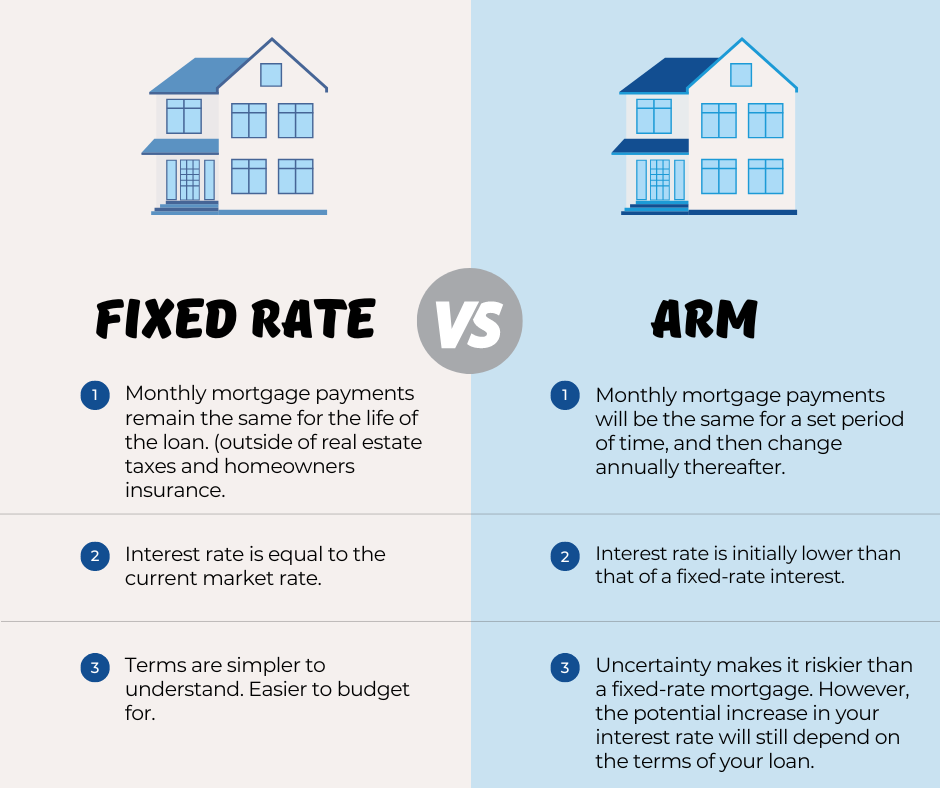
A fixed-rate mortgage means your interest rate and monthly payments stay the same for the entire loan term (usually 15, 20, or 30 years).
Pros:
- Predictable monthly payments
- Easier to budget long-term
- Protection from rising interest rates
Best for:
- Buyers planning to stay in their home for many years
- People who prefer stability and long-term budgeting
2. What Is an Adjustable-Rate Mortgage (ARM)?
An ARM starts with a lower interest rate for a few years (usually 3, 5, 7, or 10 years), then adjusts periodically based on market rates.
Pros:
- Lower initial interest rate
- Lower payments during the fixed period
- Can save money if you move or refinance early
Cons:
- Monthly payments can rise after the fixed period
- Harder to predict long-term costs
Best for:
- Buyers who plan to move or sell within a few years
- People expecting higher income in the future
3. Key Differences:
| Feature | Fixed-Rate Mortgage | Adjustable-Rate Mortgage (ARM) |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate | Stays the same | Changes after fixed period |
| Monthly Payment | Fixed | Can increase or decrease |
| Initial Rate | Usually higher | Lower during intro period |
| Risk Level | Low | Higher after adjustment |
| Good for Long-Term Stay | Yes | Not ideal |
4. How to Choose the Right One
Ask yourself:
- How long will I stay in this home?
- Can I handle payment increases in the future?
- Do I want stable payments or lower early costs?
- Is the current interest rate low or high?
Rule of thumb:
- If you plan to stay 7+ years, a fixed-rate is safer.
- If you plan to stay less than 5 years, an ARM may save money.
Conclusion
Both fixed and adjustable-rate mortgages have their advantages. A fixed-rate offers long-term stability, while an ARM gives short-term savings. The best choice depends on your budget, timeline, and risk comfort. Before deciding, talk to a mortgage advisor and run the numbers.





